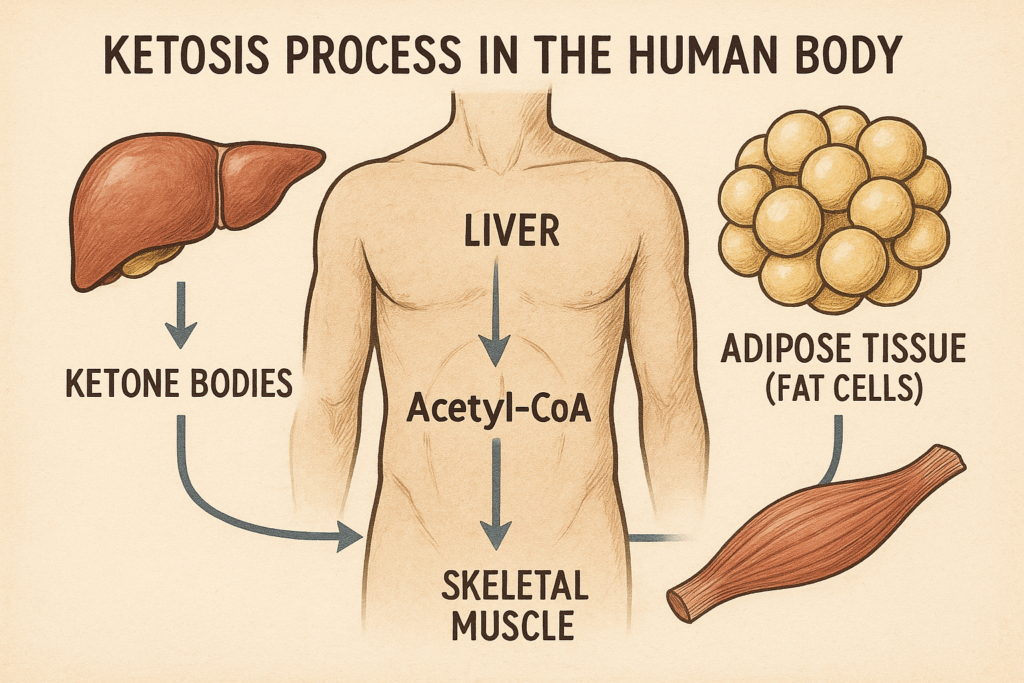
What is Inflammation?
Inflammation is the body’s natural immune response to injuries, infections, or irritations.
It’s a crucial defense mechanism that helps the body protect itself against invading agents, such as bacteria and viruses, while also promoting the repair of damaged tissues.
Inflammation is generally classified into two types: acute and chronic.
Acute inflammation is an immediate response to wounds or infections.
During this phase, the immune system activates specific cells and increases blood flow to the affected area, leading to symptoms like redness, swelling, and pain.
On the other hand, chronic inflammation is more concerning.
It occurs over a prolonged period and may last for months or even years.
Chronic inflammation is often linked to serious conditions such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and arthritis.
In these cases, the body keeps sending immune cells to the affected area even in the absence of actual threats, causing tissue damage and widespread health issues.
Diet plays a significant role in regulating inflammation.
Foods high in processed sugars and saturated fats can worsen inflammation, while anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can help fight it.
High stress levels and a sedentary lifestyle are also known to aggravate inflammation.
Awareness of these factors is essential to managing inflammation and promoting better health.

“Let your food be your medicine and your medicine be your food” is a phrase from Hippocrates, the father of medicine. More than 2,000 years later, it’s still the purest truth.”
Top 10 Anti-inflammatory Foods
While inflammation is the body’s natural reaction to injury and infection, chronic inflammation can lead to several diseases.
That’s why it’s important to focus on foods with anti-inflammatory properties.
Here are ten of the most effective foods known to reduce inflammation and support overall health:
Turmeric – Contains curcumin, a powerful anti-inflammatory compound proven to block the production of inflammatory molecules.
Ginger – Packed with gingerol, which has both anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Studies show it reduces inflammation markers.
Berries – Strawberries, raspberries, and blueberries are high in anthocyanins, antioxidants that combat oxidative stress and inflammation.
Fatty Fish – Salmon, sardines, and herring are rich in omega- fatty acids, which have potent anti-inflammatory effects.
Extra-Virgin Olive Oil – Loaded with antioxidants and healthy fats, this oil has proven anti-inflammatory benefits for cardiovascular health.
- Nuts – Especially walnuts, which contain healthy fats and antioxidants that have been linked to reduced inflammation.
Broccoli – A cruciferous vegetable with sulforaphane, an antioxidant that helps lower inflammation.
Green Tea – Rich in polyphenols, especially EGCG, which has been shown to exert strong anti-inflammatory effects.
Garlic – Contains sulfur compounds that help regulate immune function and reduce inflammation.
Spinach – A dark leafy green full of vitamins and antioxidants that contribute to reducing chronic inflammation.
Incorporating these foods into a balanced diet can significantly reduce inflammation and support a healthier lifestyle.

“Fruits low in sugar and good fats are allowed, such as berries, coconut, and avocado.”
How Anti-inflammatory Foods Work in the Body
Inflammation is a natural bodily reaction to harmful stimuli, but when it becomes chronic, it can contribute to disease development. Anti-inflammatory foods play a critical role in modulating this response through bioactive compounds that combat chronic inflammation.
Antioxidants, found in fruits and vegetables, neutralize free radicals, which are known to worsen inflammation.
- Vitamin C-rich foods like oranges and strawberries and vitamin E sources like nuts and seeds can reduce inflammatory markers and support cell recovery.
Polyphenols, present in green tea, berries, and cocoa, help regulate inflammatory gene expression and reduce the production of cytokines, fostering an anti-inflammatory state. Experts suggest that including polyphenols in the diet may prevent diseases linked to chronic inflammation.
Essential fatty acids, particularly omega-3s from fish and flaxseed, are well-known for reducing inflammation and supporting heart health. Their ability to block inflammatory substances makes them a core component of an anti-inflammatory diet.
In short, adopting a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods is a powerful strategy to improve overall health and minimize the risks associated with chronic inflammation.
Consumption Tips and Practical Advice
Integrating anti-inflammatory foods into your daily routine is an effective way to combat chronic inflammation and improve your health. Here are some easy and practical suggestions:
Combine multiple anti-inflammatory ingredients into flavorful meals. For instance, a dish with quinoa, broccoli, and avocado offers a solid base of anti-inflammatory nutrients. Enhance flavors with turmeric and ginger for an extra boost
Try nutritious smoothies by blending berries (like strawberries and raspberries) with spinach. This not only increases your intake of anti-inflammatory foods but also provides a fresh, energizing start to the day. Add chia or flax seeds for omega-3 support
Consistency matters. Aim to include at least one serving of anti-inflammatory foods in every meal. The regular Consumption of fatty fish like salmon and sardines has been linked to lower inflammation levels
Just as important as adding good foods is reducing harmful ones. Cut back on refined sugars, processed grains, and trans fats—these are known to spike inflammation.
Finally, small lifestyle adjustments like regular exercise and stress reduction can amplify the benefits of an anti-inflammatory diet and help you take control of your long-term health.
Other articles you might like!